What exactly is a Voice Application Server?
A Voice Application Server is a carrier-class Unified Communications software platform that has been optimized in terms of performance and scalability. These servers are hosted by service providers and connected to the mobile network to enable calls to a common network.
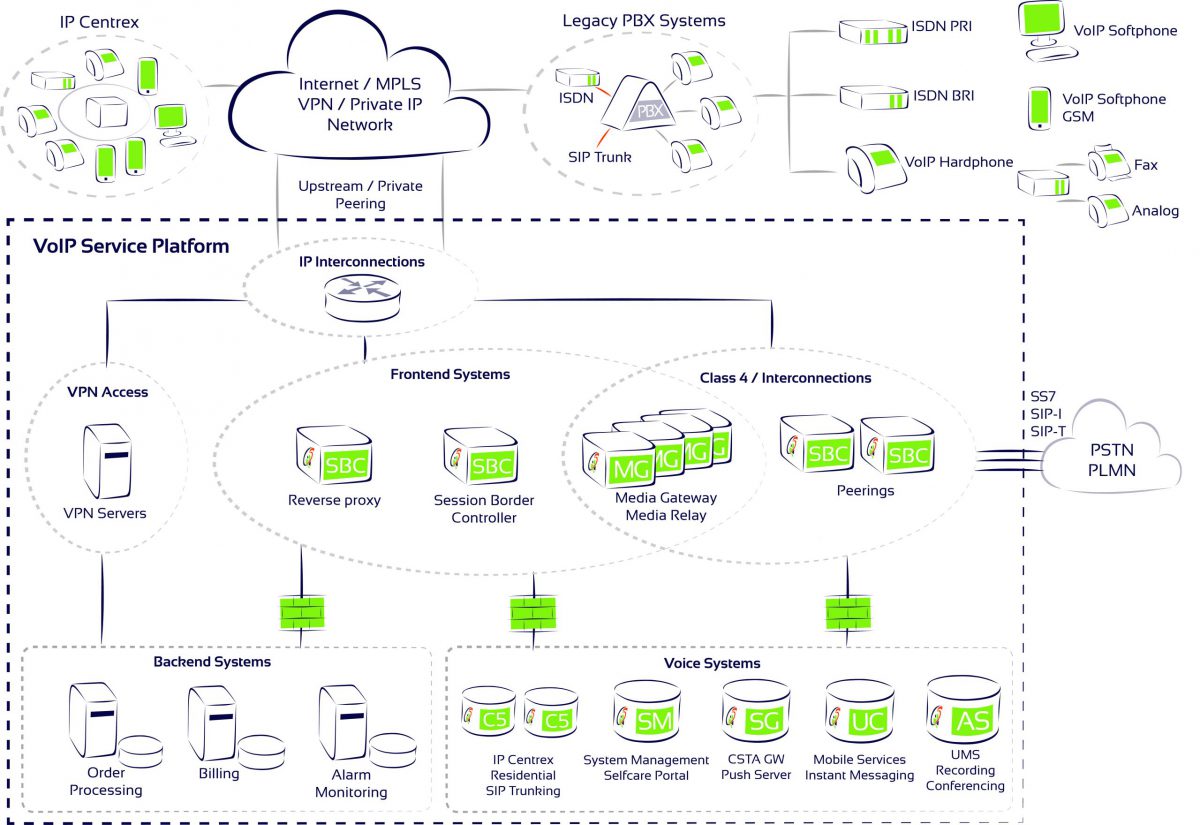
The Voice Application Server can be deployed in a single business service or a combination of cloud PBX (IP centrex), mobile PBX, business SIP trunking and consumer VoIP applications. Service providers can access the various functions, including call control and unified messaging, from a single multi-client system.
Advantages at a glance
▪ Pioneering standards-based platform. The Voice Application Server is deployed in the service provider’s network and is a combination of the best functions from several solutions.
▪ It runs on Linux systems and is supported by conventional server hardware and virtual machines.
▪ It was developed based on standards, and uses interfaces based on IETF, ETSI and other industry RFCs. This makes it easy to integrate into existing networks.
▪ The emphasis is on high scalability and reliability. The Voice Application Server can be distributed in different cities and countries, even continents, and operated as a cluster.
▪ With this application, service providers can create a cloud service that will be of interest to companies of any size thanks to easy management and uncomplicated operation.
▪ Collaboration and user productivity are top of the must-have list when choosing a communications system. By supporting so many types of devices, the application more than meets these needs.
▪ Our Voice Application Server offers web-based service management with five different administrative levels and a system API for easy integration into a company’s business processes. The resulting flexibility enables support for resellers and the integration of third-party products.
Voice Application Server – Development Interface
▪ SIP / SIPREC interface – our Voice Application Server supports RFC-based SIP and SIPREC signaling methods for a comprehensive integration with compatible systems, applications and devices. IP phones, calling apps (PC, mobile phones), switchboard apps, analog terminal adapters, SIP media gateways, IP PBXes, Session Border Controllers (SBC), call recording apps, are among the most common applications using SIP signaling.
▪ RESTful-APIs (REpresentational State Transfer) allows resources to be addressed using JASON over HTTP. Different apps or middleware services can be developed with REST to automate ordering processes or configuration tasks.
▪ CSTA (Computer Supported Telecommunications Applications) enables call control by external applications. Real-time notifications are created when an application subscribes to one or more events from a catalogue of event packages.
▪ CDR interfaces – the Voice Application Server supports the transmission of billing data. Files containing CDRs are sent over a TCP stream in real-time, or are retrieved from a file system.
▪ SNMP interfaces – Voice Application Servers provide notifications and alarm messages with alarm correlation for external management applications that use SNMPv2.
▪ HID interfaces – various PC and mobile device applications use the HID-compatible interface signaling for answer, mute and volume regulation.
Summary
The Voice Application Server was developed for service providers, to enable them to migrate existing services quickly and easily using cloud architecture. The interfaces in the open architecture allow value-added services to be offered to customers, where they can be integrated into the core network containing the required business processes (OSS/BSS).


